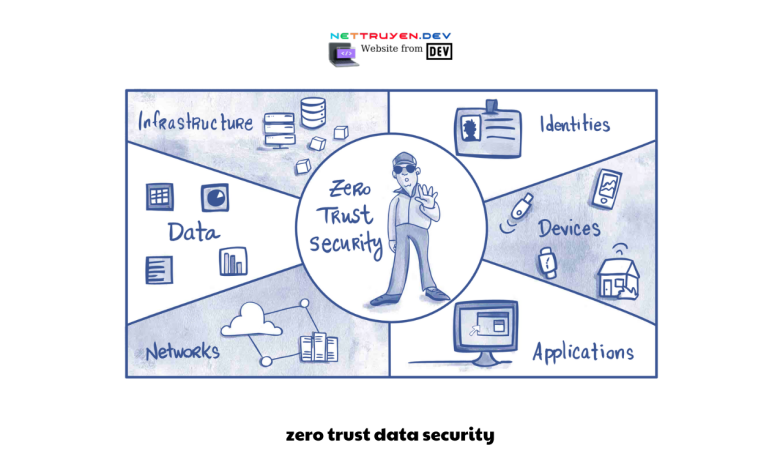
In today’s digital landscape, organizations face a constant barrage of cyber threats and data breaches. Traditional security models that rely on perimeter defenses are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive information. As a result, a new approach called “Zero Trust” has emerged as a paradigm shift in data security. In this article, Nettruyendev will explore Zero Trust data security and how it redefines protection in the digital age. By moving away from the outdated notion of trust and adopting a more proactive and comprehensive approach, organizations can enhance their defense against ever-evolving cyber threats.
Zero Trust Data Security: Redefining Protection in the Digital Age
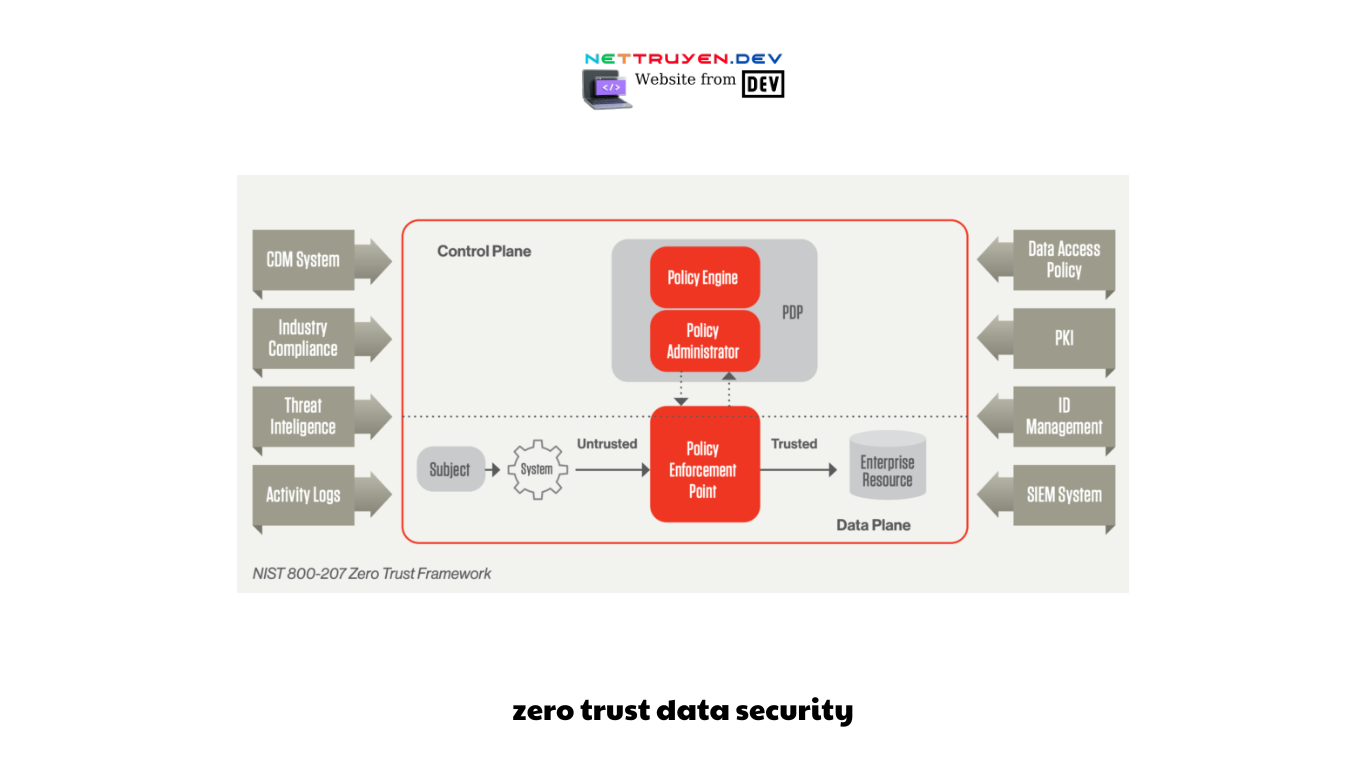
- The Evolution of Data Security:
Data security has evolved significantly over the years. In the past, organizations relied on perimeter-based security models, which assumed that internal networks were secure and trusted. However, with the rise of sophisticated attacks and the increasing number of insider threats, this trust-based approach has proven to be insufficient. Zero Trust data security challenges the traditional model by removing the inherent trust and assuming that no user or device should be automatically trusted, regardless of their location or network.
- The Core Principles of Zero Trust:
Zero Trust data security is founded on several core principles that redefine the way organizations approach cybersecurity. Firstly, it assumes that every user, device, and network is potentially compromised or malicious. Secondly, it enforces strict access controls and verification mechanisms, requiring continuous authentication and authorization for every transaction. Thirdly, it promotes the concept of least privilege, granting users only the necessary access privileges for their specific tasks. Lastly, it emphasizes continuous monitoring, analysis, and response to detect and mitigate potential threats in real-time.
- The Role of Identity and Access Management (IAM):
Identity and Access Management (IAM) plays a crucial role in implementing Zero Trust data security. By adopting robust IAM solutions, organizations can enforce strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication, and implement granular access controls based on user roles and responsibilities. IAM systems also facilitate the continuous monitoring and analysis of user behavior, enabling organizations to detect suspicious activities and respond promptly.
- Continuous Monitoring and Analytics:
A key aspect of Zero Trust data security is continuous monitoring and analytics. Traditional security models often rely on periodic security checks and static rules, which can miss or overlook emerging threats. In contrast, Zero Trust emphasizes real-time monitoring of network traffic, user behavior, and system logs. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms are employed to detect anomalies, identify potential threats, and trigger immediate responses.

- Micro-Segmentation and Network Security:
Micro-segmentation is another critical component of Zero Trust data security. Instead of relying solely on perimeter defenses, organizations implement network segmentation to divide their infrastructure into smaller, isolated segments. Each segment has its own access controls, ensuring that even if one segment is compromised, the rest of the network remains protected. Micro-segmentation provides an additional layer of security and helps to contain potential breaches.
- Zero Trust and Cloud Security:
As organizations increasingly embrace cloud computing, Zero Trust data security becomes even more relevant. Cloud environments are highly dynamic and require a comprehensive security approach that goes beyond traditional perimeter-based models. Zero Trust principles can be applied to cloud security by implementing strong identity and access controls, continuous monitoring, and encryption. By adopting a Zero Trust mindset, organizations can securely leverage the benefits of cloud computing while safeguarding their data.
- Building a Zero Trust Culture:
Implementing Zero Trust data security is not just a technological shift; it requires a cultural change within organizations. It involves educating employees about the importance of security, promoting a security-first mindset, and encouraging responsible use of technology. Regular security awareness training, incident response drills, and clear policies and procedures are essential components of building a Zero Trust culture.
- Zero Trust Challenges and Considerations:
While Zero Trust data security offers compelling benefits, organizations must also be aware of the challenges and considerations involved. Implementing Zero Trust requires significant planning, resources, and coordination across different departments and stakeholders. Legacy systems and applications may need to be updated or replaced to align with Zero Trust principles. Additionally, organizations must strike a balance between security and user experience to ensure that stringent access controls do not impede productivity.
- The Future of Zero Trust:
The concept of Zero Trust data security continues to evolve as technology advances and threats become more sophisticated. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to play a more significant role in automating threat detection and response within a Zero Trust framework. Additionally, the integration of Zero Trust principles with emerging technologies such as blockchain and secure hardware chips may further enhance data security in the future.
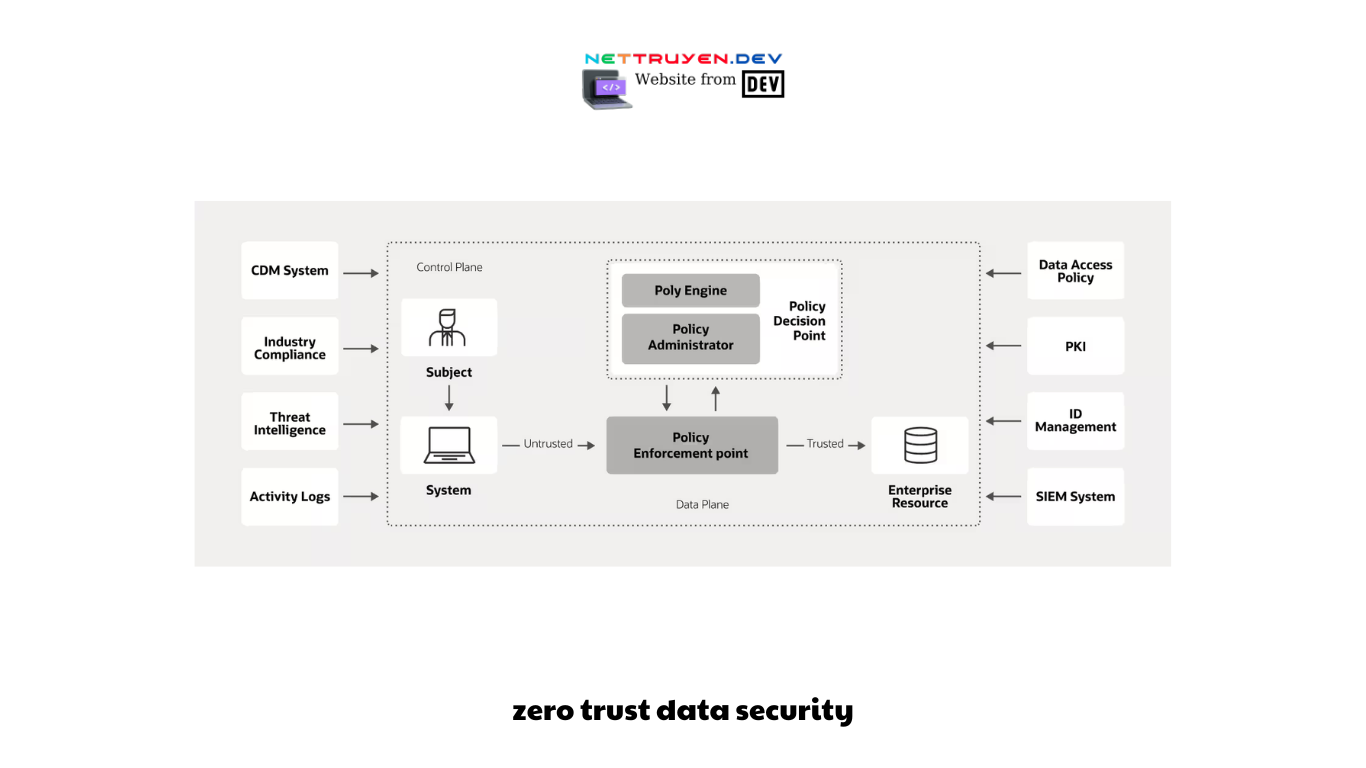
- Conclusion: Redefining Data Security:
In conclusion, Zero Trust data security represents a paradigm shift in how organizations protect their sensitive information. By eliminating blind trust and adopting a proactive and comprehensive approach, organizations can significantly enhance their defense against evolving cyber threats. Through the principles of continuous authentication, least privilege, and continuous monitoring, Zero Trust data security provides a robust framework for safeguarding data in thedigital age. By embracing technologies such as identity and access management, continuous monitoring and analytics, and micro-segmentation, organizations can build a strong security foundation.
However, implementing Zero Trust requires careful planning, resource allocation, and cultural change. As technology continues to evolve, the future of Zero Trust holds the promise of even stronger data security measures. Ultimately, Zero Trust data security redefines protection in the digital age, enabling organizations to stay one step ahead of cyber threats and safeguard their most valuable asset: their data.
Conclusion: So above is the Zero Trust Data Security: Redefining Protection in the Digital Age article. Hopefully with this article you can help you in life, always follow and read our good articles on the website: nettruyen.dev
Related Articles
-
A Comprehensive Exploration of Secure Data SharingDecember 4, 2023




